Renova Plastic surgery clinic
Gynecomastia
(removal of mammary glands in men)
(removal of mammary glands in men)
The lack of treatment for gynecomastia or the low effectiveness of conservative therapy leads to the long-term
existence of pathology, where there is a risk of the disease degenerating into cancer.
Surgery to remove excess tissue solves this problem.
existence of pathology, where there is a risk of the disease degenerating into cancer.
Surgery to remove excess tissue solves this problem.
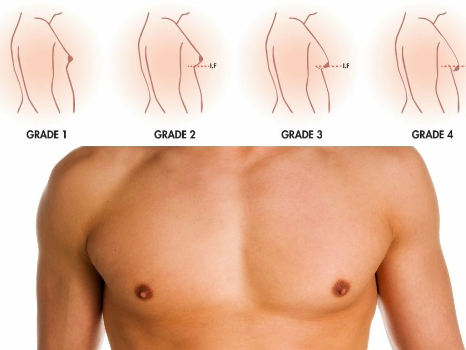
Male gynecomastia. The mammary glands become enlarged - one or both - due to the growth of glandular or adipose tissue. Each gland with such a disease can increase up to 15 cm. In adolescent boys and the elderly, pathology occurs in 70% of cases, in young ones - in 40%.
Female gynecomastia is more rare.
Usually, this diagnosis is made when the breast volume exceeds 400 mm3.
The disease can be accompanied by discomfort and other unusual and unpleasant sensations.
Male breasts can increase for several reasons:
fat deposition due to pituitary adenoma, hormonal imbalance, smoking, drug addiction, alcoholism, trauma, cardiovascular insufficiency, HIV, etc.
False and true gynecomastia
External these two types of disease hardly different.
First, seals form in the nipple area, then gradually the breast grows according to the female type. The nipples are pulled out, the hair on the chest is falling out.
With a false pathology, the mammary glands enlarge due to the accumulation of fat, and not glandular tissue, as in the true one.
The combined type is often diagnosed, but the female bust consists of 90% of adipose tissue, for this reason the false type of the disease is more noticeable, the man's chest becomes more expressive, "female".
Female gynecomastia is more rare.
Usually, this diagnosis is made when the breast volume exceeds 400 mm3.
The disease can be accompanied by discomfort and other unusual and unpleasant sensations.
Male breasts can increase for several reasons:
fat deposition due to pituitary adenoma, hormonal imbalance, smoking, drug addiction, alcoholism, trauma, cardiovascular insufficiency, HIV, etc.
False and true gynecomastia
External these two types of disease hardly different.
First, seals form in the nipple area, then gradually the breast grows according to the female type. The nipples are pulled out, the hair on the chest is falling out.
With a false pathology, the mammary glands enlarge due to the accumulation of fat, and not glandular tissue, as in the true one.
The combined type is often diagnosed, but the female bust consists of 90% of adipose tissue, for this reason the false type of the disease is more noticeable, the man's chest becomes more expressive, "female".
- suspected cancer;
- the formation of a tumor, cyst, nodes in the breast;
- stable one-sided form of pathology;
- mixed or true type of disease that does not respond to conservative therapy;
- the discomfort that a man experiences, his desire to correct his appearance;
- pain that bothers the patient constantly
Average duration - 1-1.5 hours (in difficult cases - more), local anesthesia is used.
Excess tissue is removed by surgical excision, alone or in conjunction with liposuction. Access is through incisions around or above the nipples. Excess skin and fat are also removed. If the excess tissue is large, the incisions are enlarged.
During liposuction, cannulas are inserted into the incisions that have already been made, into the chest fold or the armpit area.
Liposuction is performed at the initial stage, and then the doctor excises the excess tissue.
After the operation, drainage is usually installed in the affected area, and an elastic tight bandage is applied to the patient.
Excess tissue is removed by surgical excision, alone or in conjunction with liposuction. Access is through incisions around or above the nipples. Excess skin and fat are also removed. If the excess tissue is large, the incisions are enlarged.
During liposuction, cannulas are inserted into the incisions that have already been made, into the chest fold or the armpit area.
Liposuction is performed at the initial stage, and then the doctor excises the excess tissue.
After the operation, drainage is usually installed in the affected area, and an elastic tight bandage is applied to the patient.
In the first days, there is pain, which is relieved by painkillers as prescribed by a doctor, and a feeling of heaviness in the operated area. Also, relatively pronounced hematomas and swelling are normal. The stitches are removed after 7-10 days. An elastic bandage should be worn constantly for the first 7-14 days, and then only at night. The exact time and mode of wearing it for the patient will be indicated by the doctor.
Puffiness disappears in the first weeks, but a stable result is formed after at least 3 months.
After 2-3 weeks, massage can be done. It speeds up healing. Only a doctor prescribes it.
The process of scar stabilization lasts about a year, during which they can be red, slightly protrude above the skin.
Puffiness disappears in the first weeks, but a stable result is formed after at least 3 months.
- In the first 1-2 weeks, you can not carry weights, raise your hands up. It is recommended to sleep on your back.
- For 4-5 days, you need to refuse to take a shower.
- For 1.5 months, there is a ban on physical activity.
- In the first 2-3 months, you should not sunbathe, overheat (go to the bathhouse, sauna). It is better to exclude sunburn for 6 months in order to eliminate the risk of pigmentation in the areas of surgical wounds.
After 2-3 weeks, massage can be done. It speeds up healing. Only a doctor prescribes it.
The process of scar stabilization lasts about a year, during which they can be red, slightly protrude above the skin.
- 37 years of the experienceTime-tested quality results
- 20+ years of plastic practiceworld-class practitioners, constantly undergoing advanced training
 Clients from all over the WorldSwitzerland, Holland, Germany, France, Sweden, USA, Italy, England, Slovakia, Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and many others
Clients from all over the WorldSwitzerland, Holland, Germany, France, Sweden, USA, Italy, England, Slovakia, Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and many others- 7,000+ satisfied patientsOur top priority is the health and comfort of our patients
Sign up for a consultation to
Dr. Ahmed Said
Dr. Ahmed Said
"Restore harmony inside yourself and out"
Guest Reviews
Services











